Features of Indian Federalism
Features of Indian Federalism
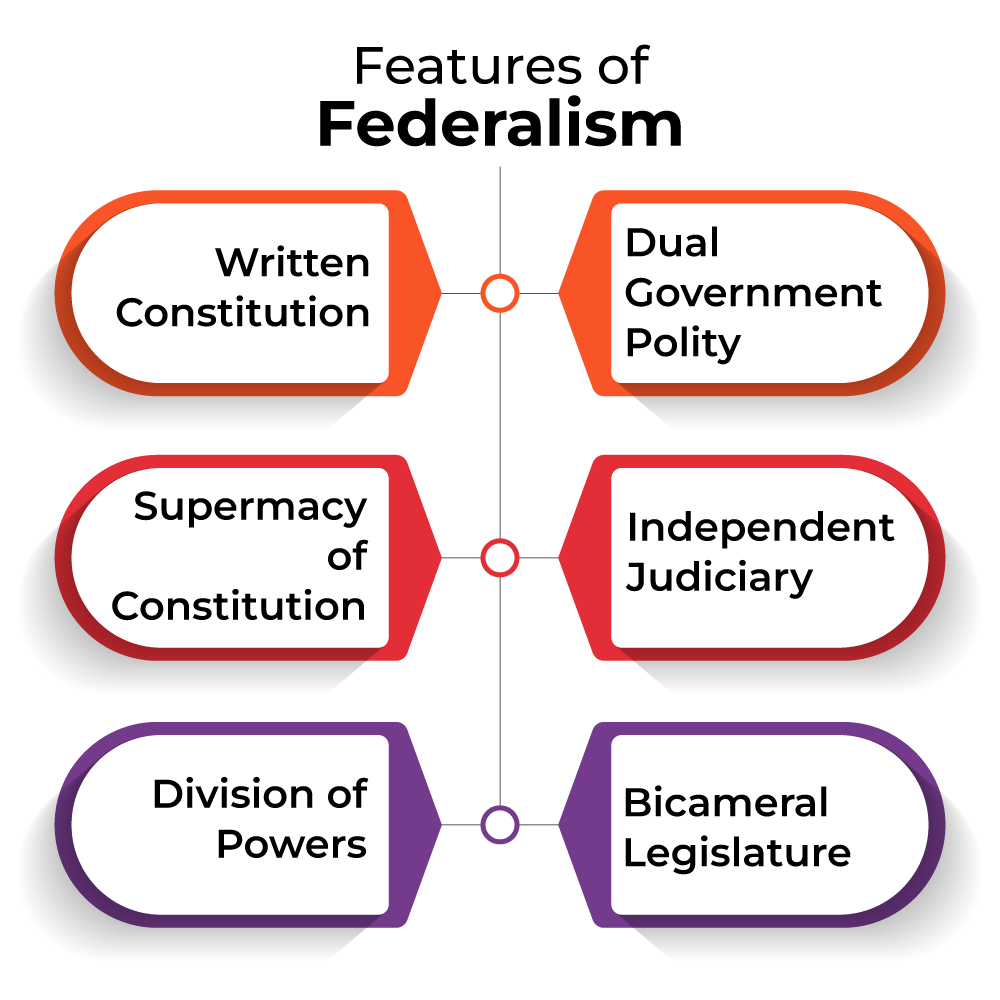
There are certain unique features in Indian federalism. They are as follows:
- Supreme and single constitution: Constitution is the most supreme law of the land in India. It contains several components that together act as a rule of thumb in framing policies of the government. It guarantees a set of fundamental rights to the citizens. Similarly it demarcates the domains of power of executive, legislative and financial powers of both the governmen t of India and the states.
- Dual government: The constitution has distributed powers between the Union and the States. Through this distribution, it seeks to accommodate the diversity of India. By providing certain powers to the state governments, the constitution allows the states to take decision with flexibility and according to local needs.
- Authority of the courts: Legal supremacy of the constitution is an essential feature in the federal system. It helps in maintaining the division of powers between the union and centre. Courts have the final power to interpret the constitution and nullify actions on the part of the federal and state governments or their different units, which violate the provisions of the constitution.
- Mode of formation: Unlike the United States, which was formed as a result of coming together of a group of states, Indian federalism was born out of the need for administrative convenience.
- Position of the states in the federation: In the United States, since the states had existed much before the formation of federation, they held their own sovereignty vis-a-vis the federal government. Therefore, their constitution had several safeguards for the protection of state's sovereignty. Whereas in India, there was no such history of states holding a higher sovereignty. Thus, our states do not enjoy a higher authority in comparison to the Union government.