India TB Report-2024
India TB Report-2024
GS-2: Health Issues
(UPSC/State PSC)
Important for Prelims:
Contemporary issues related to TB and India TB Report-2024, Union Health Ministry, WHO Report, Nikshay Portal, Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan, Nikshay Poshan Yojana, In-Country Model.
Important for Mains:
India TB Report 2024 – Key Facts, About Tuberculosis (TB), Major Initiatives of Government of India to eliminate TB, Global Initiatives, Conclusion.
29/03/2024
Why in news:
Recently, the Union Health Ministry has released the ‘India TB Report 2024’.
India TB Report 2024:
- The following facts were presented in this report released on March 27, 2024:
- Unidentified cases: There were only 2.3 lakh unidentified cases in the year 2023, while in the year 2022 the number was 3.2 lakh.
- Ni-Kshaya Portal: According to the government's Ni-Kshaya portal, the gap between estimated and actual cases of TB in India is decreasing due to continuous monitoring of all TB patients.
- Comparison between private and government health centres: Most of the TB cases are still reported by government health centres, even though there has been an increase in notifications by the private sector.
- Of the 25.5 lakh cases reported in 2023, about 33% or 8.4 lakh cases came from the private sector.
- To compare, only 1.9 lakh cases were registered by the private sector in 2015
- Increase in projected incidence: The projected incidence of TB in 2023 increased slightly to 27.8 lakh from last year's estimate of 27.4 lakh.
- Death rate: According to statistics, the death rate due to infection remains at 3.2 lakh.
- India specific data: India reached its 2023 target of initiating treatment in 95% of patients suffering from the infection.
- It said 58% of those diagnosed were offered testing to check whether their infection was resistant to first-line drugs, up from 25% in 2015.
- These estimates are based on a new methodology, in-country models.
What is In-Country Model:
- It is a sophisticated mathematical model to track and evaluate the prevalence of TB cases in India.
- This model has been developed by India and India has become the first country in the world to develop this model.
- This model has also been recognized by WHO.
- It is based on the natural history of the disease, individual cases of infection, health care, treatment coverage and outcome.
About India TB Report:
- It is an annual report prepared and published by the Central TB Division of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India, under the National TB Elimination Program (NTEP).
- Published since 2001, this report presents key data and analysis on the status of TB in India.
Major initiatives of the Government of India to eradicate TB:
- The Government of India has set a target of eliminating TB from India by the year 2025.
- Prime Minister TB Free India Campaign
- Prime Minister TB Free India Campaign was launched in September 2022.
- It has made TB a topic of public discussion, thereby creating awareness among people about this disease.
- Under the government programme, TB patients are provided free screening, free treatment, tests and free medicines at all public health centres.
- ‘Nikshay Nutrition Scheme’
- In the year 2018, the Central Government launched Nikshay Poshan Yojana, which aimed to help every TB patient by providing a Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) of Rs 500 per month for nutritional needs.
- National Strategic Plan (NSP) for Tuberculosis Elimination (2017-2025)
- Nikshay Ecosystem (National TB Information System)
- ‘T.B.Harega, Desh Jitega Abhiyan.
- Development of Vaccines:
- Currently two vaccines have been developed for the treatment of tuberculosis: VPM (Vaccine Project Management) 1002 and MIP (Mycobacterium indicus prani).
- Currently these vaccines are being tested in Phase-3.
- According to the Global TB Report 2023 published by WHO,
- The rate of TB cases in India has declined by 16% from 237 per 100,000 population in 2015 to 199 per 100,000 population in 2022.
- During the same period, the TB mortality rate has declined by 18% from 28 per 100,000 population in 2015 to 23 per 100,000 population in 2022.
Global Initiative:
- Global Fund and Stop TB by WHO. A joint initiative with the partnership “Find. Treat. All. #EndTB” has been started.
- World Health Organization also releases 'Global Tuberculosis Report'.
Other reasons for improvement in TB cases:
- The following factors can be attributed to the improvement in TB cases;
- Increasing awareness about TB disease among people.
- Providing better treatment facilities by the government.
- Increasing cooperation between public and private health services.
- Speeding up the investigation process.
WHO End TB Strategy:
- It was adopted in 2014 with the aim of ending the TB epidemic globally by 2035.
Target:
- It aims to reduce the number of TB deaths by 95% by 2035 compared to 2015.
- To reduce TB incidence rate by 90% by 2035 compared to 2015.
- To reduce the number of families facing devastating costs due to TB to zero by 2035.
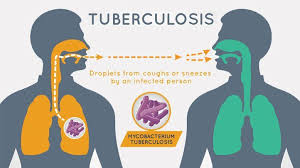
About Tuberculosis (TB):
- It is a serious respiratory disease, also known as tuberculosis. This bacterial infection is especially caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria.
- In TB disease, the lungs are most affected by the infection.
- When a person suffering from this disease comes in contact with the droplets released by coughing and sneezing, the chances of another person getting infected also increases.
Symptoms of TB:
- Most people do not show any symptoms in the initial stages of infection.
- Some people develop flu-like problems, causing mild fever, fatigue and cough.
- In case of increased infection, problems like phlegm coming with cough, pain with breathing or coughing, fever-chills, sweating at night are seen.
Conclusion:
- TB is an infectious disease, so it is important to break the infection cycle to stop the spread of the disease.
Source: The Hindu
--------------------------------------
Mains Question:
According to India TB Report 2024, TB cases are under control in India. Explain its main causes.