
Kyasanur Forest Disease
15.04.2025
Kyasanur Forest Disease
|
For Prelims: About Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD) |
Why in the news?
Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD), or "monkey fever," is currently surging in Karnataka's Shivamogga and Chikkamagaluru districts recently.
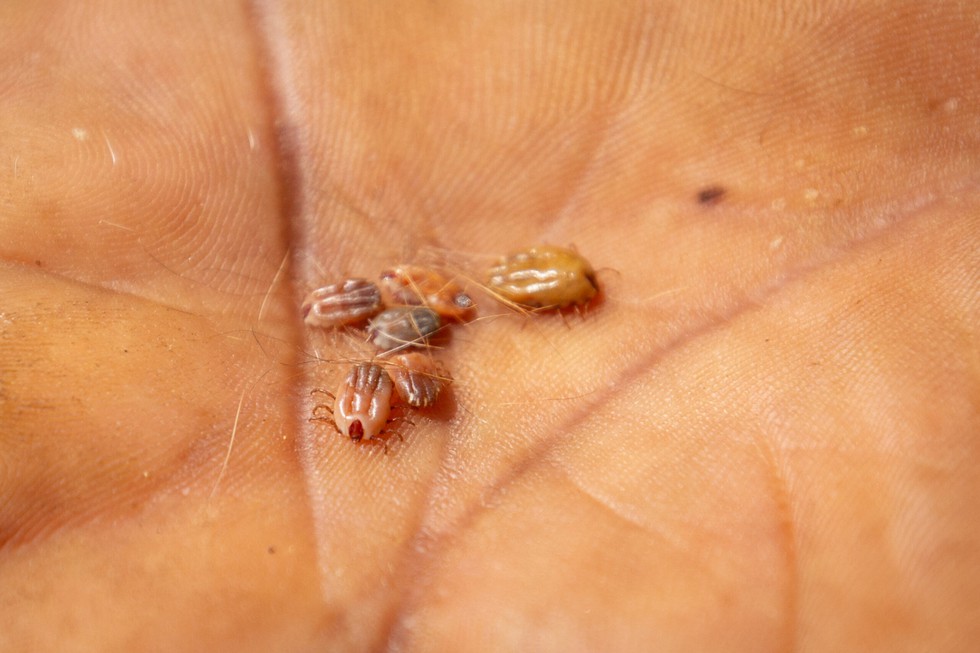
About Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD):
- KFD, also referred to as Monkey Fever, is a tick-borne viral haemorrhagic disease, which can be fatal to humans and other primates.
- It is mostly found in southern India. The disease was first reported from the Kyasanur Forest of Karnataka in 1957, hence, it is known as KFD.
- The causal agent, Kyasanur Forest Disease Virus (family Flaviviridae, genus Flavivirus), is a member of the tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) complex.
- The epidemic period usually begins in October or November and peaks from January to April, then declines by May and June.
Transmission of the disease:
- Hard ticks (Hemaphysalis spinigera) spread the KFD virus to people and to animals, like monkeys and rodents.
- No person-to-person transmission has been established yet.
Symptoms of the disease:
- Most people with KFD have a sudden onset of chills, fever, and headache.
- Severe muscle pain, vomiting, gastrointestinal symptoms, and bleeding can follow 3 or 4 days after symptoms begin.
- Most patients recover one to two weeks after symptoms begin.
- About 10 to 20% of patients experience a second wave of symptoms, including severe headache, mental disturbances, tremors, and vision problems.
- Between 5 and 10% of people who are known to be affected by KFD die.
Treatment of the disease:
- There is no cure for KFD.
- Supportive care is crucial, including fluid balance, providing oxygen, managing blood pressure, and treating additional infections.
- Vaccine: A vaccine for KFD is available and recommended in the parts of India where KFD is found.
- The existing vaccine is a formalin-inactivated whole virus vaccine, but it requires booster doses and has shown limited efficacy in some cases.
Source: The Times of India
Consider the following statement regarding the Kyasanur Forest Disease:
1.The disease was first reported from the Kyasanur Forest of Karnataka in 1957.
2.It also referred to as Monkey Fever, is a tick-borne viral haemorrhagic disease
3.It is mostly found in southern India.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
A.Only one
B.Only two
C.All three
D.None
Answer C