
Prison Manuals and Reforms
09.12.2025
Prison Manuals and Reforms
Context
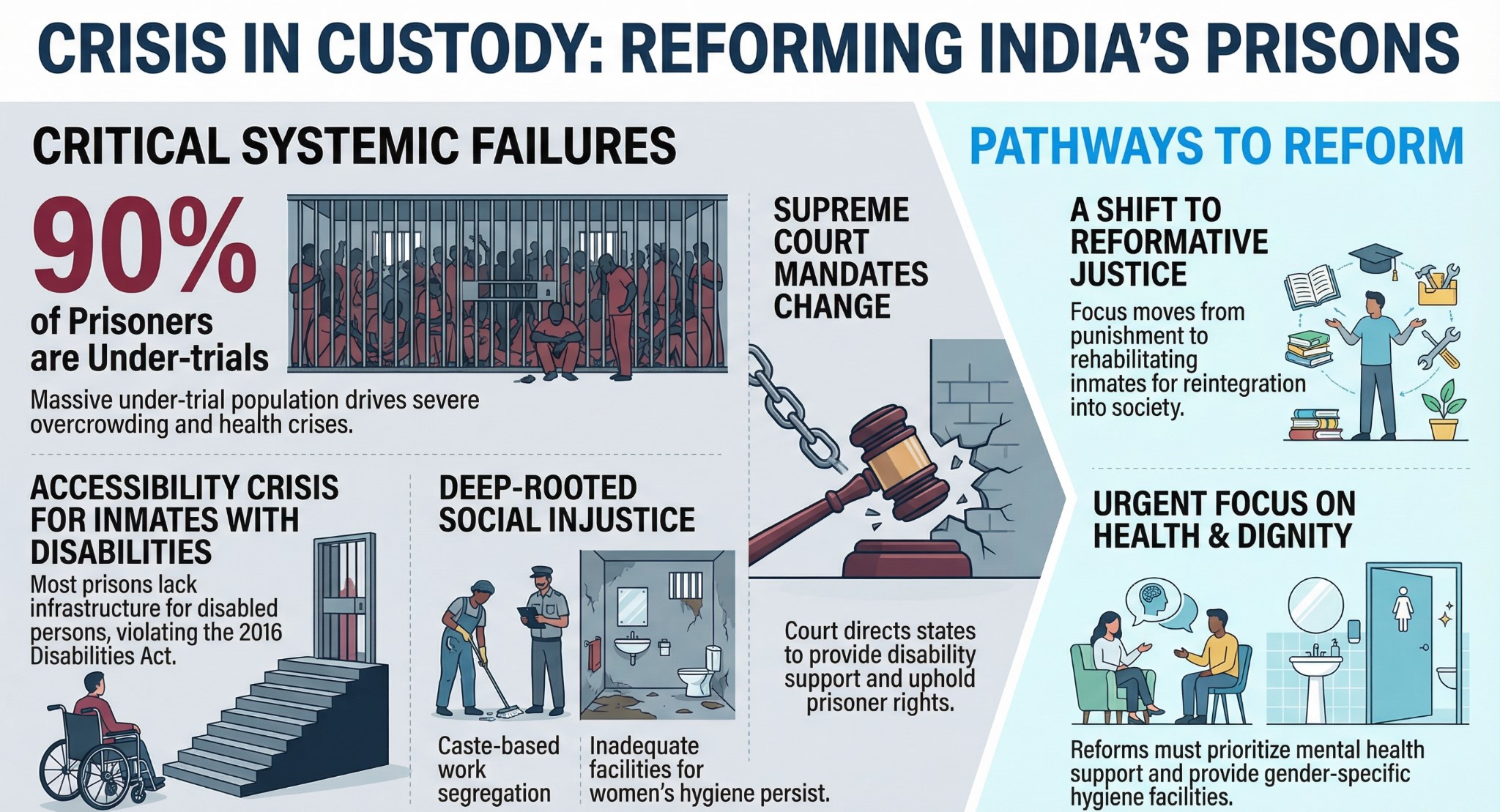
The administration of prisons in India faces significant scrutiny following Supreme Court observations regarding the rights of prisoners, particularly those with disabilities. Since "Prisons" fall under the State List of the Seventh Schedule, the Union Government can only issue advisory directions, not mandatory instructions, making uniform reform challenging.
Rights of Persons with Disabilities (Divyang Jan) Accessibility Crisis:
- Infrastructure Deficit: Most Indian jails are not designed to accommodate Divyang Jan (Persons with Disabilities), creating severe physical barriers.
- Legal Mandate: The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 mandates support systems, yet implementation in prisons remains poor.
Judicial Intervention:
- Supreme Court Directions: Citing cases like those of Stan Swamy and G.N. Saibaba, the Court has directed authorities to provide necessary disability-related support.
- State Negligence: There are ongoing issues where the State has delayed or denied allowances requested by inmates with serious physical conditions to cope with incarceration.
Major Areas for Reform Structural and Health Issues:
- Overcrowding: A critical issue that exacerbates the spread of contagious diseases, including HIV/AIDS.
- Under-trial Population: Approximately 90% of India's prison population consists of under-trials. The Supreme Court reiterates the principle that "bail should be the rule, and jail the exception."
Social Justice Concerns:
- Caste-Based Segregation: Several states continue to follow discriminatory colonial manual rules, such as reserving sanitation and cleaning work specifically for Dalit and Adivasi prisoners. Courts have deemed this practice unconstitutional.
- Gender-Specific Needs: Reforms are required to address women's hygiene and dignity, specifically the provision of separate washrooms and sanitary pads.
Rehabilitation and Mental Health:
- Mental Health: The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) highlights mental health as a significant concern among inmates requiring urgent psychiatric support.
- Reformative Justice: The justice system aims to shift focus from purely punitive measures to reformative justice, helping inmates rehabilitate and reintegrate into society.
Conclusion
Prison reform in India requires a multi-faceted approach, moving beyond confinement to ensure human dignity. Addressing the high volume of under-trials, eliminating caste-based labor, and ensuring accessibility for disabled prisoners are essential steps to align prison administration with constitutional values.