
New Approach for Green Hydrogen Production
01.05.2025
New Approach for Green Hydrogen Production
|
For Prelims: What is Green Hydrogen? Key Scientific Findings, Mechanism of Proton Adsorption, Green Hydrogen Production Methods |
Why in the news?
Researchers at the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, have developed new insights into proton adsorption on catalyst surfaces, paving the way for more efficient green hydrogen production.
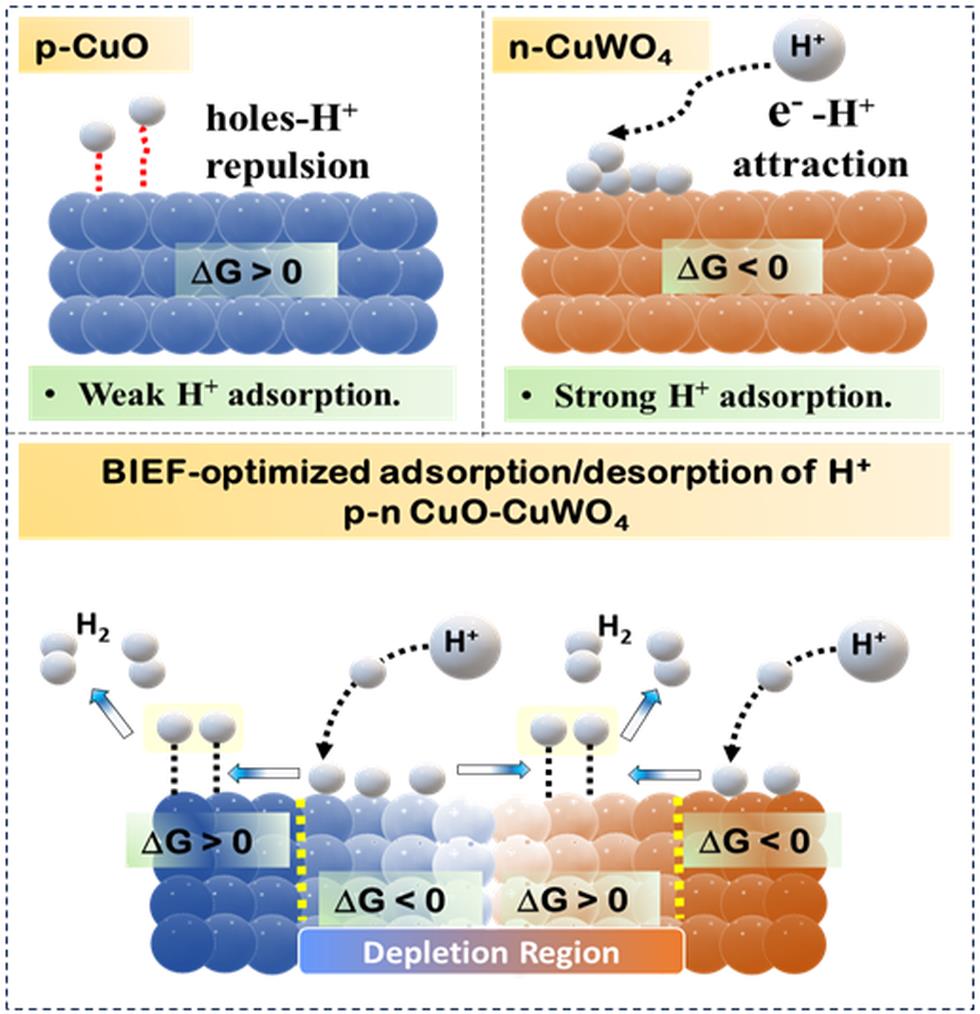
Key Scientific Findings:
- A novel heterostructure, combining Copper Tungsten Oxide (CuWO₄) and Copper Oxide (CuO), has been created to exploit the Built-In Electric Field (BIEF) effect for enhanced hydrogen evolution.
- The structure is formed by growing CuWO₄ nanoparticles over a Cu(OH)₂ precursor, leading to a p-n heterojunction that creates an asymmetric electronic environment.
- This BIEF plays a crucial role in modulating proton adsorption and desorption, directly influencing the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction (HER)
Mechanism of Proton Adsorption:
- The interface between CuO and CuWO₄ shows variation in Gibbs Free Energy (∆G), especially near the depletion region.
- A gradient in ∆G across this interface enhances hydrogen adsorption at CuO and desorption at CuWO₄, making the system more favourable for HER.
- This showcases "negative cooperativity", where increased proton binding at one site reduces affinity at other sites, facilitating proton desorption, a key step in alkaline hydrogen production.
What is Green Hydrogen?
- It is produced through the electrolysis of water using renewable energy sources like solar, wind, or hydropower, releasing no greenhouse gases.
- It is a clean, sustainable, and flexible energy carrier, with water vapour as its only by-product.
- Unlike grey hydrogen (from fossil fuels), green hydrogen contributes to zero carbon emissions.
Green Hydrogen Production Methods:
- Alkaline Electrolysis: Mature, low-cost method using KOH/NaOH; needs nickel/platinum
- Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Electrolysis: High efficiency, fast, but expensive due to precious metal catalysts.
- Solid Oxide Electrolysis (SOEC): Works at 700–1000°C, enables co-electrolysis of H₂O and CO₂, but involves complex materials and high costs.
Source: PIB
With reference to the Green Hydrogen, consider the following statements:
Statement-I: It is produced through the electrolysis of water using non- renewable energy.
Statement-II: It is a clean, sustainable, and flexible energy carrier.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
A.Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I.
B.Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I.
C.Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect.
D.Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct.
Answer D