
Global Gender Gap Report (2024)
14.06.2024
Global Gender Gap Report (2024)
|
For Prelims: About the Global Gender Gap Index (2024), Key Findings of the Report, India’s Performance |
Why in the news?
Recently, the World Economic Forum (WEF) published the 18th edition of the Global Gender Gap Report (2024).
About the Global Gender Gap Index (2024)
- It annually benchmarks the current state and evolution of gender parity across four key dimensions, i.e. Economic Participation and Opportunity; Educational Attainment; Health and Survival, and Political Empowerment.
Key Findings of the Report
- The global gender gap score in 2024 for all 146 countries included in this edition stands at 68.5% closed.
○It means that on average, across the world, there is still a 31.5% gender gap that needs to be closed.
○Compared to the constant sample of 143 countries included in last year’s edition, the global gender gap has been closed by a further +0.1 percentage point, from 68.5% to 68.6%.
- Based on current data, it will take 134 years to reach full parity, which is roughly five generations beyond the 2030 Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) target.
○The lack of meaningful, widespread change since the last edition effectively slows down the rate of progress to attain parity.
- Top Performers: While no country has achieved full gender parity, 97% of the economies included in this edition have closed more than 60% of their gap.
○It is a significant improvement compared to 85% in 2006.
○Iceland (1st, 93.5%), alongwith the Finland (2nd, 87.5%), Norway (3rd, 87.5%), Sweden (5th , 81.6%), Germany (7th, 81%), Ireland (9th, 80.2%) and Spain (10th, 79.7%) has been leading the index for a decade and a half.
○Finland continues to be the only economy to have closed over 90% of its gender gap.
- Globally, Sudan was ranked last on the index of 146 countries, while Pakistan slipped three places to 145th.
- Gender parity in labour-force participation has shown some improvement. According to data from 101 economies tracked since 2006, the participation rate has rebounded from 63.5% in 2023 to 65.7% in 2024.
India’s Performance
- India, with a population of over 1.4 billion, closed 64.1% of its gender gap in 2024. However, India has slipped two places to 129th place (127th last year), mainly because of small declines in ‘Educational Attainment’ and ‘Political Empowerment,’ parameters, while ‘Economic Participation’ and ‘Opportunity’ scores slightly improved.
- India showed the best gender parity in terms of enrolment in secondary education.
- In the Political Empowerment sub-index, India scored within the top-10 on the head-of-state indicator, but its scores for women’s representation at the federal level, in Ministerial positions (6.9%) and in Parliament (17.2%), remain relatively low.
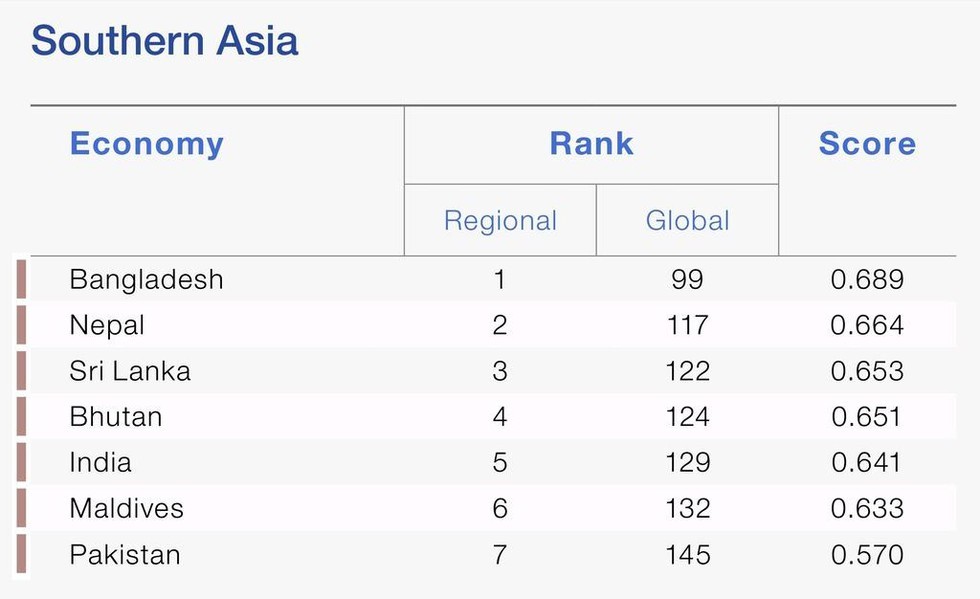
- Within South Asia, India was ranked fifth after Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka and Bhutan, while Pakistan was ranked last.
- India figured among the economies with the lowest levels of economic parity, alongside Bangladesh, Sudan, Iran, Pakistan, and Morocco. All of them registered less than 30% gender parity in estimated earned income.
Source: The Hindu
Ques :- The Global Gender Gap Report 2024 is released by which one of the following?
A.World Bank
B.World Economic Forum (WEF)
C.United Nations (UN)
D.International Monetary Fund (IMF)
Answer B