Extreme Challenges of Inflation in India
Extreme Challenges of Inflation in India
Main Examination: General Studies Question Paper-3
(Food Inflation)
September 19, 2023
Why in News:
- Recently, according to the price index of the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), food prices in India have been recorded as relatively high in relation to large economies globally.
- At present, rising inflation is costing the common man dearly. The challenge of inflation may become more difficult with crude oil prices reaching the highest level in the last ten months at more than $ 93 per barrel due to the decision of Saudi Arabia and Russia to cut oil production amid concerns about the supply of food items. In such a situation, reducing inflation has become a big issue for the government.
About Food Inflation:
- Food inflation is an economic term that refers to the general increase in prices of food items.
- It is an important factor in the cost of living, as food is a basic necessity for life.
- Food inflation can lead to a reduction in the purchasing power of a household's income as well as an overall increase in poverty.
- It particularly affects the general public of the country, as food constitutes a large part of the average household budget.
Current situation of inflation:
- According to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), inflation had reached a high level in July 2023 due to supply chain fluctuations.
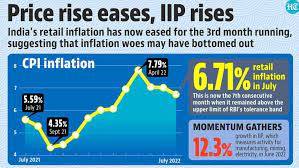
- According to the Consumer Price Index (CPI), the retail inflation rate reached 4.87 percent in June 2023 and the fifteen-month high of 7.44 percent in July.
- Retail inflation had declined slightly to 6.8 percent in August 2023.
- Due to rising prices of food items, the retail inflation rate is higher than the upper limit of six percent set by the Central Government.
- RBI has increased the estimate of retail inflation rate for the current financial year 2023-24 to 5.4 percent.
Causes for increase in food prices:
- Grain prices increased due to lack of rain in major food producing areas
- At present, many reasons are visible for the sharp increase in food prices.
- Grain prices have increased due to Russia's decision to end the Black Sea grain agreement and reduced wheat storage and lack of rain in key food producing areas.
- Vegetables have become expensive due to whitefly infestation on crops in the country and uneven distribution of monsoon rains.
- Wholesale wheat prices in the country have increased sharply in the last two months due to limited supply.
- There has also been a decrease in wheat stocks in government warehouses.
- Inflation has also increased due to excess cash in the market.
- Due to the dominance of El Nino this time, meteorologists have said that India's monsoon will end by September 30 with less than normal rainfall i.e. 94 percent. According to meteorologists, El Nino is likely to remain in this condition till March-April next year.
Efforts to control rising inflation:
- The Central Government and RBI have made several efforts to control the rising inflation due to food prices in the country.
- On August 29, the Central Government has given a big relief by reducing the price of domestic LPG cylinder by two hundred rupees.
- In the bi-monthly review meeting of the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of RBI held on August 24, an important decision was taken to keep the interest rate at 6.5 percent due to the rising prices of tomatoes and other vegetables.
- The Central Government is continuously taking strict action against the export of food items. The ban on wheat exports that was imposed after the start of the Russia-Ukraine war last year due to low production is still in place.
- The government has fixed the minimum price for export of Basmati rice at $ 1200 per tonne. Forty percent export duty has been imposed on onion.
- The Center has also imposed twenty percent duty on the export of boiled rice from August 25.
- The government is trying to control the rising prices of wheat and rice.
- Therefore it is selling both wheat and rice at concessional rates through Open Market Sale Scheme (OMSS).
- Similarly, special measures have also been taken to control the prices of vegetables, pulses and oilseeds.
- In order to reduce the import cost of petrol and keep the price low, the government is mixing ten percent ethanol in petrol.
- The situation is that despite various efforts to control inflation, food inflation has not yet come under control. The Finance Ministry, in its July report, has also warned that inflation may remain high in the coming months due to global and regional uncertainties and supply disruptions within the country.
- Controlling inflation is also important because its high rate not only causes problems for the common man but also affects economic development.
- In such a situation, the government will have to come forward with more effective measures to increase the supply of food items and curb retail inflation.
- Although the prices of petrol and diesel have declined in the last fifteen months, their prices in the market remain the same.
- In May 2022, the price of crude oil was around $ 110 per barrel, which is currently $ 93 per barrel.
Way Forward:
- To control rising inflation, the limit and excise duty on petrol and diesel should be reduced by the central government and VAT by the state governments.
- Immediate action should be taken against those who hoard in the country.
- Appropriate storage limits should also be imposed for wholesale and retail traders of food items. The Reserve Bank will have to pay attention to the withdrawal of excess cash.
- Like the exemption in import of crude oil from Russia, India can also get exemption on import of wheat. Increasing import of pulses can also reduce the inflation of pulses.
- In this perspective, the foreign exchange reserves of $ 595 billion that India had in August 2023 can also play an important role in controlling inflation.
- After the export control steps taken in India to prevent rising food prices, many global organizations including the International Monetary Fund (IMF) are demanding withdrawal of restrictions imposed on the export of important food items from India.
- Globally, food experts are saying that the protection strategy adopted by the government in India to control domestic prices of food items has further increased food inflation in the world.
- India is the world's largest exporter of rice and its share in the world market is forty percent. India is the second largest exporter of sugar and onion. In such a situation, due to export control by India, their prices have started increasing in the world.
- Even though most of the countries in the world are currently criticizing India's inflation control measures due to concerns about controlling inflation in their respective economies, India too has to take care of its own interests before worrying about global inflation.
- The Government of India and the Reserve Bank will also have to keep in mind that especially to control the prices of food items, the government will have to make such provisions so that the supply of essential commodities is not disrupted.
- The government should strategically form a price control committee, which, keeping in mind the fluctuations in the market, takes appropriate price control steps before the prices go out of control.
----------------------------------------
Mains Exam Question
Suggest rational measures to control the rising food inflation in the country.