Free Movement Regime (FMR) on India Myanmar Border
Free Movement Regime (FMR) on India Myanmar Border
GS-II, III: International Relations, Internal Security
(UPSC/State PSC)
January 27, 2024
Important for Prelims
India-Myanmar border, Free Movement Regime (FMR), Act East policy, Illegal immigration, ethnic violence and insurgency.
Important for Mains
About India-Myanmar border, need of FMR with Myanmar, about Free Movement Regime (FMR), importance of free movement Regime, challenges, conclusion.
Context:
- Recently, the Union Home Ministry has decided to erect fencing along the entire length of the India-Myanmar border to prevent free movement of people.
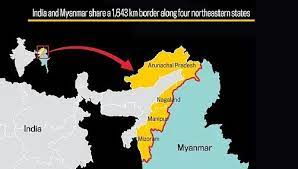
India-Myanmar Border:
- The 1,643 km border between India and Myanmar touches four states: Mizoram, Manipur, Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh.
- It is an open range that runs through wooded and undulating terrain, it is almost entirely unfenced and difficult to monitor.
- In Manipur, less than 6 km of the border has been fenced.
Need of FMR with Myanmar:
- Illegal Immigration: To control illegal uncontrolled immigration of Chin people from Myanmar.
- Entry of troops from Myanmar: To control the migration of junta troops in search of refuge in Mizoram.
- Ethnic violence and insurgency: The Meitei community attributed last year’s tensions to the perceived illegal migration of tribal Kuki-Chin communities.
- Surge in drug production in Myanmar: Linked to Myanmar’s political turmoil, has security implications for the region (report by UNODC).
Future of Free Movement Regime (FMR) and Border Management:
- Balancing Security and Local Needs: Experts doubt its effectiveness without proper border security and enforcement. They suggest regulating FMR rather than complete removal or fencing the entire border.
- Manipur’s suspension of the FMR since 2022 hasn’t significantly altered the situation.
- Alternatives to FMR: Improved border management, intelligence gathering, and addressing the root causes of migration in Myanmar are crucial.
- Bilateral Cooperation: Collaboration with Myanmar is essential for effective border management and tackling shared security challenges.
About Free Movement Regime:
- The Free Movement Regime is a mutually agreed arrangement between the two countries that allows tribes living along the border on either side to travel up to 16 km inside the other country without a visa.
- It is commonly associated with regional integration efforts where member states agree to facilitate the movement of individuals without imposing strict visa requirements or other barriers.
- The primary goal is to promote economic, social, and cultural cooperation among participating nations. Several regions around the world have implemented free movement regimes.
- It was implemented in 2018 as part of the government’s Act East policy.
Significance of Free Movement Regimes:
- Visa-Free Travel: Citizens of member states can travel freely within the region without the need for visas or with simplified visa procedures.
- Residence Rights: Some agreements allow citizens to live and work in any member state without additional permits.
- Removal of Border Controls: Borders within the region may be open, with the elimination of passport controls and customs checks.
- Harmonization of Policies: Member states often work towards aligning immigration, labor, and social policies to facilitate seamless movement.
- Economic Integration: Free movement regimes are often part of broader economic integration efforts, fostering cooperation in trade, investment, and other economic activities.
Challenges:
- Security Concerns: Ensuring the free movement of people while addressing security challenges, such as illegal immigration and transnational crime, requires careful management.
- Socioeconomic Disparities: Disparities in economic development among member states can lead to concerns about potential imbalances in the labor movement.
- National Sovereignty: Some nations may be hesitant to fully embrace free movement regimes due to concerns about preserving national sovereignty and identity.
- Public Perception: Public sentiment and political considerations can influence the success and sustainability of free movement agreements.
Conclusion:
- Free movement regimes represent a significant step toward regional integration, fostering closer ties among nations and contributing to economic and social development. However, the success of such regimes depends on effective coordination, shared objectives, and the ability to address associated challenges.
Source: The Hindu
----------------------------------------------
Mains Question:
How does the 'free movement regime' on the India-Myanmar border contribute to the internal security challenge of ethnic violence in the North-Eastern states?
What is 'free movement regime '? Throw light on its need and significance.