Shortened TB Treatment Plans for India’s TB Burden
Shortened TB Treatment Plans for India’s TB Burden
GS-3: Health (UPSC/State PSC)
Why in news:
According to recent studies, short-term treatments may be effective in treating TB.
- This treatment shows effectiveness in both adults and children.
- Urgent adoption of these innovative treatments by India is crucial to enhance TB management.
- For drug-sensitive TB, the patient must take the drug for six months, and for most people this is a long period of time.
- Tuberculosis treatment poses challenges due to long, difficult medication regimens.
What is Tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is a dreadful disease with a high mortality and has consistently been a global health concern.
Its causes
- Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria usually attack the lungs, but TB bacteria can attack any part of the body such as the kidney, spine, and brain.
- Not everyone infected with TB bacteria becomes sick. As a result, two TB-related conditions exist: latent TB infection (LTBI) and TB disease.
- If not treated properly, TB disease can be fatal.
Its symptoms
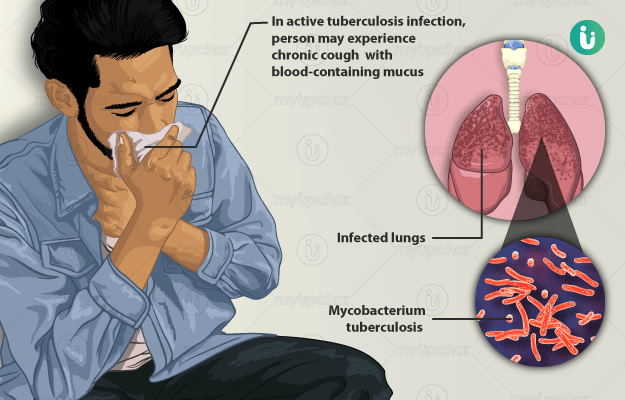
- Symptoms of TB disease depend on where in the body the TB bacteria are growing.
- TB bacteria usually grow in the lungs (pulmonary TB). TB disease in the lungs may cause symptoms such as:
- a bad cough that lasts 3 weeks or longer,
- pain in the chest
- coughing up blood or sputum (phlegm from deep inside the lungs)
- Other symptoms of TB disease are
- weakness or fatigue
- weight loss
- no appetite
- chills
- fever
- sweating at night
- Symptoms of TB disease in other parts of the body depend on the area affected.
What is India’s TB burden?
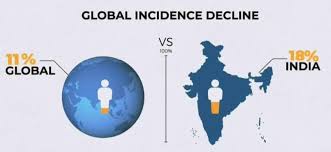
- India accounts for around 27% of TB cases worldwide – which is the world’s highest country-wise TB burden – thanks in part to its population of 1.3 billion.
- Nearly 28.2 lakh people got TB in India in 2022, meaning one person gets TB every 11 seconds in India, according to The Global TB report 2023.
- India’s contribution to the global burden is 27%, which is down one percentage point from the previous year’s 28%.
What is India’s TB elimination target?
- India has set a target of 2025 for eliminating TB in the country. The national strategic plan 2017-2025 sets the target of no more than 44 new TB cases per lakh population by 2025.
- The 2023 report pegs this number at 199 cases per lakh. Achieving this target is a big task as the plan had envisaged an incidence of only 77 cases per lakh population by 2023.
- The programme also aims to reduce the mortality to 3 deaths per lakh population by 2025.
- Even with the WHO accepting the lowered estimates for India, this stands at 23 per lakh population.
India’s Initiatives towards TB elimination
- India has undertaken several initiatives towards TB elimination including active case finding, scaling up of more accurate molecular testing to block level, screening services made available through the health and wellness centres, and engagement of the private sector as well.
- According to The Union Health Ministry Ni-kshay Mitra where people provide additional nutritional support to TB patients has also resulted in the adoption of over 11 lakh TB patients. This support is in addition to government’s R500 nutritional support.
National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP)
- In the last decade, the National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP), along with the private sector, has successfully found and treated 17.14 million people with TB, including an estimated 1.4 million children.
- However, the COVID-19 pandemic adversely affected TB care and has threatened to reverse the gains made in reducing India’s burden.
Steps taken for its mitigation
- To (re)invigorate this fight, and to align with the vision of being ‘TB Free’ ahead of the global target, India must consider active screening and case detection along with new guidelines for shorter TB treatment.
- Policymakers must also consider moving to a shorter treatment course for treating TB at the earliest. If we delay, we stand to lose the fight as well as millions of lives to an ultimately curable disease.
- An important approach, especially in high TB burden countries like India, is to explore new treatment approaches for TB and integrate them into national plans.
- With increasing political commitment in India's fight against TB, the Government of India must embrace innovation and new ways to treat this disease.
- At this time, it is up to researchers to identify the best combinations of these new drugs that are highly efficacious, minimally toxic, and can be easily implemented in programmatic settings.
Conclusion:
India’s aim to eliminate TB by 2025 is ambitious. The theme for World Tuberculosis Day (March 24) in 2023 was “Yes, we can end TB”, which reflects the worldwide desire to eliminate the disease by 2030.
Source: The Hindu
------------------------------------
Mains Question:
What is Tuberculosis? Write India’s Initiatives towards TB elimination with highlighting Steps taken for its mitigation.
I appreciate you sharing information in this blog it is are nice blog
IAS Hub Civil Service Academy
01-Jan-2024 05:45 PM