Women Labor Force and Inclusive Growth
Women Labor Force and Inclusive Growth
Important for Prelims:
Periodic Labor Force Survey Report 2022-23, Female Labor Force Participation Rate, Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation, Wage Code 2019, Social Security Code, 2020
Important for Mains:
GS-2: Causes, Challenges, Solutions for low female participation in the workforce,.
09 November 2023
Context:
A recent report shows a significant increase in the female labor force participation rate (FLFPR) in India.
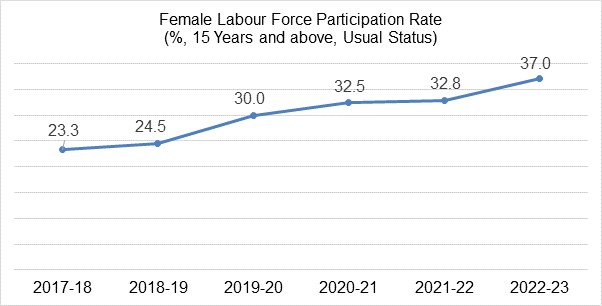
- The Periodic Labor Force Survey Report 2022-23, released by the Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation on October 9, has recorded a significant increase of 4.2 percentage points in the Female Labor Force Participation Rate (FLFPR) for the year 2023 at 37.0 per cent.
Labor force participation rate in India:
Statistics:
- The labor force participation rate in India is 42.4 percent in the year 2023, which is more than 41.3 percent in the year 2022. The average labor force participation rate in India between 1990 and 2023 is 54.2 percent. It reached an all-time high of 57.2 percent in 2000 and a low of 36.9 percent in 2018.
Female Labor Force Participation:
- Female labor force participation remained almost stable at 44.2 percent in 1993 and 44 percent in 2004, but decreased to 32.8 percent in 2011 and to a minimum of 24.8 percent in 2017, which later increased to 39.2 percent in the year 2022.
- The gap between male and female labor force participation rates increased from 49.5 percent in 1993 to 52.5 percent in 2022.
- According to the latest annual PLFS report, the labor force participation of working women in the country improved from a low of 24.8 per cent in 2017 to 30.0 per cent, 32.5 per cent and 32.8 per cent during 2019-20, 2020-21 and 2021-22 respectively.
- The participation rate of rural women decreased from 26.5 percent in 2009-10 to 25.3 percent in 2011-12, while the participation rate of urban women increased from 14.6 percent to 15.5 percent during the same period. Data for 2011–12 show that fewer women in rural areas were in work, and even if they were in work, they were in supporting or marginal employment.
Source: Periodic Labor Force Survey 2022-23
Global female labor force participation rate
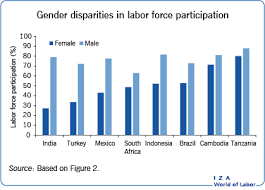
- The global female labor force participation rate has been around 52 percent for the last three decades.
- According to the International Labor Organization, female labor force participation varies greatly across developing economies.
- In North Africa, the Middle East and South Asia, less than one-third of women participate in the workforce, while in East Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa this proportion is usually two-thirds.
Cause:
- This difference is due to many reasons including cultural values, location and conservative thinking as well as socio-economic development rate, increasing educational attainment, falling fertility rate.
- Gender inequalities in the labor market are high in developing countries, but highest in South Asian countries, while the global male labor force participation rate is almost the same across all economies, at 80 percent.
Causes of low participation of women in the labor force
- The gap in labor force participation and wages is not due to biological factors, but due to unpaid family responsibilities.
- Actually, female labor force participation rate is related to economy and cultural values.
- Impacts include increasing educational enrollment of women, fertility rates, age at marriage, economic growth and urbanization, lack of employment opportunities, inaccurate measurement, and family income.
- There has been considerable progress in girls' education, the number of working women has also increased. But in the country, especially in rural areas, such jobs were not created which could easily employ women. Despite inadequate employment generation, household income increased, leading to a decline in women's participation in supporting activities.
- Although most women in India contribute to the economy in some way or the other, they are not recorded in official statistics. Many women consider household work as their work.
- In 2011-12, 35.3 percent rural women and 46.1 percent urban women were involved in domestic work, whereas in 1993-94 this rate was 29 percent and 42 percent respectively. Therefore, inaccurate measurement of the female labor force participation rate due to it not being captured in official statistics affects the trend in the data.
Challenges faced by women labor force:
- A major problem of economic development is disproportionate participation of women in the labor market and gender inequality.
- There are many problems in India for women to enter the labor market, access employment and get equal opportunities for better earning.
- Women face many challenges such as access to employment, working conditions and circumstances, employment security, unequal pay, work and family responsibilities, discrimination.
- According to Professor Claudia Goldin, winner of the Nobel Prize in Economics in the year 2023, the income and labor force participation of Indian women is lower than that of women and men in the global labor force. According to Goldin, even where women's employment is high, there are inequalities in income.
Government Efforts in India:
- The Government has taken several steps to improve women's participation in the labor force and the quality of their employment:
- Training is being provided to women through Women Industrial Training Institutes, National Vocational Training Institutes and Regional Vocational Training Institutes.
- Protective provisions have been included in labor laws for equal opportunities and favorable work environment for women workers.
- Social Security Code, 2020
- This code has provisions for increasing paid maternity leave from 12 weeks to 26 weeks, mandatory crèche facility in establishments with fifty or more employees, allowing women workers in night shifts with adequate safety measures, etc.
- There is a provision for labor protection, labor welfare and better working conditions for women workers.
- Salary Code 2019
- There shall be no discrimination by an employer in any establishment on the basis of sex in matters relating to wages, for similar work or work of a similar nature.
- An employer shall not discriminate on the basis of sex in recruiting any employee for work of a similar nature or similar work under the same conditions of employment, except where the employment of women in such work is prohibited or restricted under any law.
Solution:
- There is a need to increase female labor force participation in India and tackle gender inequality in income.
- Of the 166 million women participating in the labor force in India, 90 percent are employed in the unorganized sector, where there is a need to end their exploitation and take more effective measures for social protection.
- Policy makers should therefore adopt a comprehensive approach to improve the labor force for women through education and training programs, skill development, access to child care, maternity protection and provision, etc.
- Gender-specific barriers need to be addressed to increase female labor force participation rates and earnings equality.
- Along with increasing female labor force participation, good work opportunities should also be provided to women so that their socio-economic empowerment can take place.
- Beyond the labor force participation rate, policy-makers should be more concerned about how women will be able to take advantage of opportunities in the labor market by being able to access better jobs or start businesses.
Conclusion:
Women's participation in the labor force and their access to decent work and better incomes are essential for inclusive and sustainable development. But despite strong economic growth and rising incomes and wages in the Indian economy, women's labor force participation remains very low. Without women's participation, the overall socio-economic progress of the society comes to a halt. Society can ensure its development only through the empowerment of women.
Source-PIB
-------------------------------------------
Mains Exam Question
Despite substantial participation in the labor force, the condition of women workers in the country is pathetic. Suggest necessary solutions to improve it.